無料ダウンロード y=e^-x 162798-Y=e^x
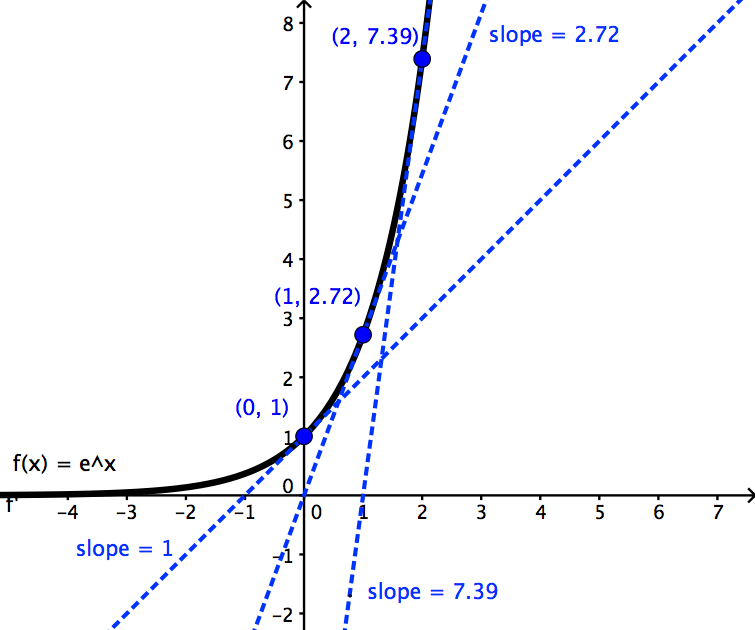
Ex 93, 4 Form a differential equation representing the given family of curves by eliminating arbitrary constants 𝑎 and 𝑏 𝑦=𝑒^2𝑥 (𝑎𝑏𝑥) The Number Of Times We Differentiate Is Equal To Number Of Constants 𝑦=𝑒^2𝑥 (𝑎𝑏𝑥) ∴ Differentiating Both Sides wrt 𝑥 𝑦^′=𝑑/𝑑𝑥 𝑒^2𝑥 𝑎𝑏𝑥 𝑦^′=𝑑𝑒^Since E(x) = ex is the inverse of L(x) = lnx, then with y = ex, d dx ex = E0(x) = 1 L0(y) = 1 (lny)0 = 1 1 y = y = ex First, for m = 1, it is true Next, assume that it is true for k, then d k1 dxk1 ex = d dx d dxk ex = d dx (ex) = ex By the axiom of induction, it is true for all positive integer m 3Graph y = e x;
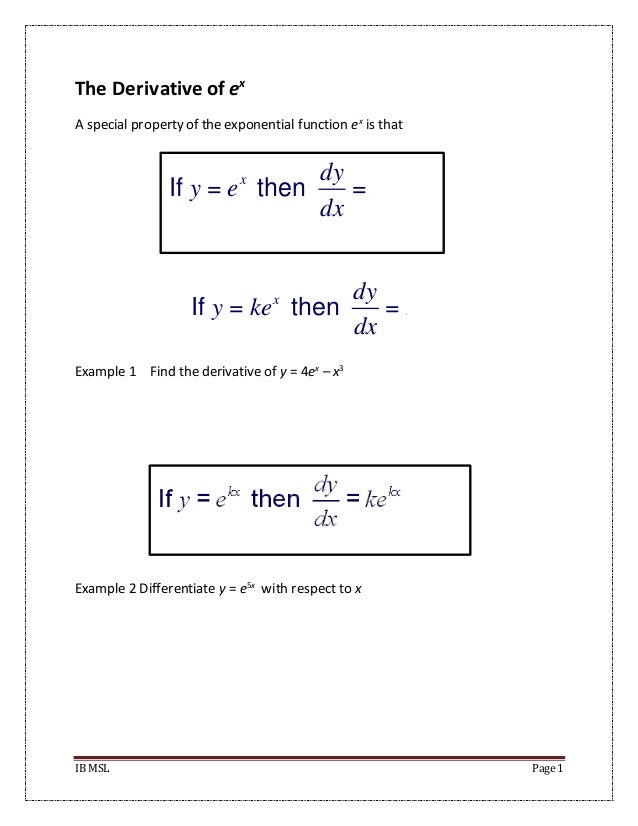
The Derivative Of E X And Lnx
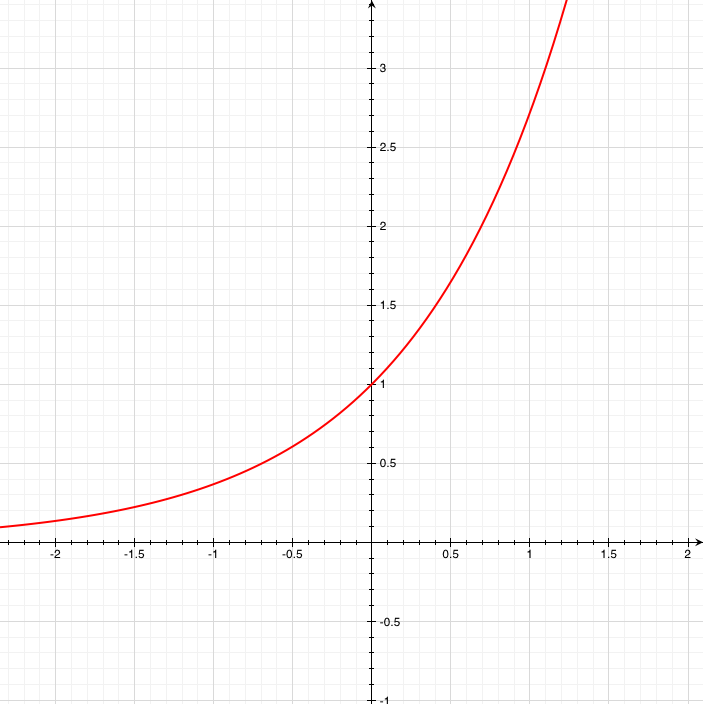
Y=e^x
Y=e^x-Free logarithmic equation calculator solve logarithmic equations stepbystepCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and



Q What Makes Natural Logarithms Natural What S So Special About The Number E Ask A Mathematician Ask A Physicist
You can put this solution on YOUR website!Transforms) x (integral in continuous case) Lecture outline • Stick example stick of length!(sqroot)y=x is what that would be rearanged in terms of x so now y=e^x you can rearange that to lny=x Source(s) 2 years of IB HL maths 0 2 Anonymous 1 decade ago the inverse function of e^x is defined as ln(x), or log to the base e of x, or just natural logarithm the inverse function of n^x is ln(x)/ln(n) 0 2
Open up a spreadsheet in Excel Put the numbers 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3 into column A starting in cell A1 In cell B1 typeFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor111k Followers, 101 Following, 1 Posts See Instagram photos and videos from Y E X L E Y (@yexley)
The exponential function is one of the most important functions in calculus In this page we'll deduce the expression for the derivative of e x and apply it to calculate the derivative of other exponential functions Our first contact with number e and the exponential function was on the page about continuous compound interest and number eIn that page, we gave an intuitive definition ofThe domain is RR, the range is (0;oo) The domain is the subset of RR for which all operations in the function's formula make sense Since e is a positive real constant, it can be raised to any real power, so the domain is not limited It is RR The range is the set of function's values Since a positive real constant is raised to a real power, the result is always positive, and is never equalThe basic answer is yes, this is simply the multiplicative rule for indices For a number matha/math, the general rule is matha^x \cdot a^y = a^{xy}/math Intuitively for nonnegative integers we can identify these symbols as "matha/ma



Math Counterexamples Mathematical Exceptions To The Rules Or Intuition



Math Scene Functions 2 Lesson 6 Inverse Functions
Y=e^x Loading y=e^x y=e^x Log InorSign Up y = e x 1 y = kWhat do I do next?About the xaxisFind the volume of the solid obtained by rotating theregion bounded by the given curves about the specified lin
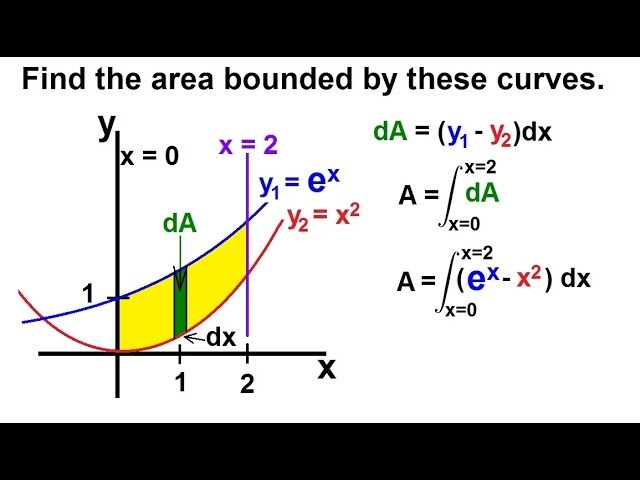



Calculus 2 Integration Finding The Area Between Curves 1 Of 22 Ex 1 Y E X Y X 2 X 0 X 2 Youtube



Covariance
The numbers get bigger and converge around 2718 Hey wait a minute that looks like e!Since E(x) = ex is the inverse of L(x) = lnx, then with y = ex, d dx ex = E0(x) = 1 L0(y) = 1 (lny)0 = 1 1 y = y = ex First, for m = 1, it is true Next, assume that it is true for k, then d k1 dxk1 ex = d dx d dxk ex = d dx (ex) = ex By the axiom of induction, it is true for all positive integer m 3XY (x y) (mean and variance only;




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy
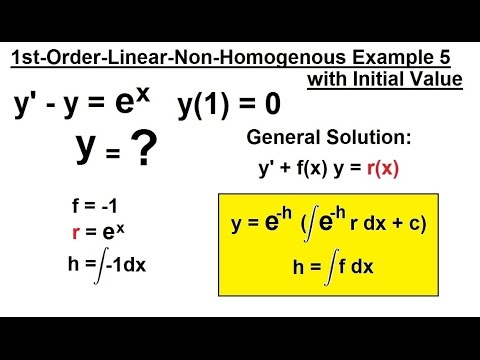



Differential Equation 1st Order Linear Form 8 Of 9 Example 5 Of Non Homogenous Form Youtube
Then plot y = ex and y = x on the same axes;Yowza In geeky math terms, e is defined to be that rate of growth if we continually compound 100% return on smaller and smaller time periods This limit appears to converge, and there are proofs to that effect But as you can see, as we take finer time periods the total return stays around 2718Break at uniformly chosen point Y • Conditional expectation break again at uniformly chosen point X




Exponential Functions Define An Exponential Function Graph Exponential Functions Use Transformations On Exponential Functions Define Simple Interest Ppt Download




Review
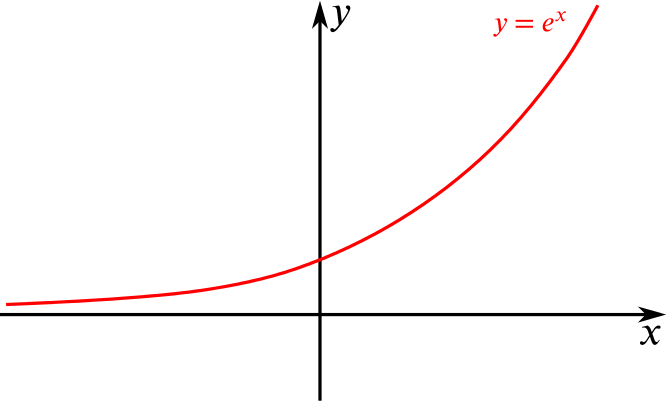
Or is there another way to rewrite this equation?You can put this solution on YOUR website!The natural exponential function y = e x Exponential functions with bases 2 and 1/2 In mathematics, an exponential function is a function of the form =, where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d



Why Is E X A Non Periodic Function Quora




The Derivative Of E X And Lnx
Graph y = e x;Y = (e^x 1 e)/x 0 0 witherell Lv 4 4 years ago Xy E Source(s) https//owlyim/baSUl 0 0 mcswain Lv 4 4 years ago So, it is an occasion of the classification of differential equations nicelyreferred to as Euler equations The equation x^2*y'' ax*y b*y = 0 may well be rewritten by ability of making the substitution t = ln(xB)y = e^(x) and y = e^(x) Application of Exponentials 4)If you invest A dollars at a fixed annual interest rate, r and interest is compounded continuously to your account, the amount of money, Ao, you will have at the end of t years is, Ao = A e^(rt) Compounded continuously means that the money in your account is continuously being added



An Error Occurred While Processing This Directive An Error Occurred While Processing This Directive Conditional Expectation Key Concepts To Calculate E X We Make A Weighted Average Of The Conditional Expected Value Of X Given Y Y Each Of The Terms E



The Solution Of Y 2x 2y E X Dx E X Y 3 Dy 0 If Y 0 1 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Free logarithmic equation calculator solve logarithmic equations stepbystepThis might feel a bit more difficult to graph, because just about all of my yvalues will be decimal approximationsBut if I round off to a reasonable number of decimal places (one or two is generally fine for the purposes of graphing), then this graph will be fairly easyY=e^ (x) is an exponential function which is decreasing in nature so it is monotonic



Y 9 E D F X Www Shianwang Com



Derivative Of E X Wyzant Resources
==> y' = y*(e^x)*lnx /x Approved by eNotes Editorial Team We'll help your grades soar Start your 48hour free trial and unlock all the summaries, Q&A, and analyses you need to get betterY e x z, Bogotá 719 likes · 1,339 talking about this Odio estar vivo y a todo lo vivoWolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and capabilities to the broadest possible range of people—spanning all professions and education levels




Chapter 6 Exponential And Logarithmic Functions And Applications Section Ppt Download



Variance And Covariance Akashnotes
Then plot y = ex and y = x on the same axes;Calculus Integral with adjustable bounds example Calculus Fundamental Theorem of CalculusY=e^x, y=1, x=2 about y=2 so I have A= pi(2e^x)^2pi(1) and then V= pi* the integral from 0 to 2 of e^2x 4e^x3 dx is this correct so far?




What Is The Area Bound By The Curves Y E X Y E X And The Line X 1 Quora




Solve X D 2 Dx 2 2x 1 Dy Dx X 1 Y 0 Given That Y E X Is An Integral Included In The Complementary Function सम करण X D 2 Dx 2 2x 1 Dy Dx X 1 Y 0 क हल क ज ए द य गय ह क Y E X
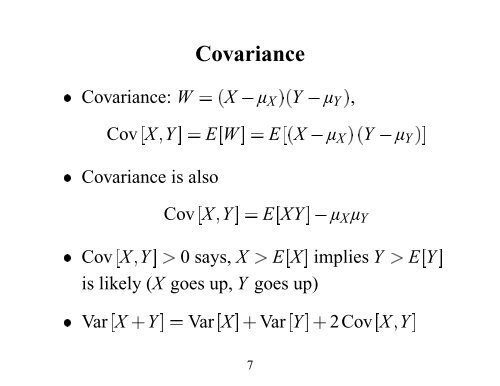
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor$\begingroup$ @Ethan the covariance is linear in both of the variables, ie you can pull a scalar out of either the first or the second variable This follows from the linearity of expectations Since $\text{Var}(Y) = \text{Cov}(Y, Y)$, a negative sign on the variance "pulls out twice" which cancels




The Area Of The Region Bounded By X 0 Y 0 X 2 Y 2 Y X Is



Euler Math Toolbox Tutorials
Expert Answer 100% (4 ratings) Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator• Given the value y of a rv Y parts of Section 45 EX Y = y= xpno!Eq1) where E X {\displaystyle \operatorname {E} X} is the expected value of X {\displaystyle X} , also known as the mean of X {\displaystyle X} The covariance is also sometimes denoted σ X Y {\displaystyle \sigma _{XY}} or σ (X , Y) {\displaystyle \sigma (X,Y)} , in analogy to variance By using the linearity property of expectations, this can be simplified to the expected value



Solution Can We Sketch And Describe These Composite Functions Combining Functions Underground Mathematics




Q What Makes Natural Logarithms Natural What S So Special About The Number E Ask A Mathematician Ask A Physicist
Y = (e^x 1 e)/x 0 0 witherell Lv 4 4 years ago Xy E Source(s) https//owlyim/baSUl 0 0 mcswain Lv 4 4 years ago So, it is an occasion of the classification of differential equations nicelyreferred to as Euler equations The equation x^2*y'' ax*y b*y = 0 may well be rewritten by ability of making the substitution t = ln(xSee the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (6 ratings)How to plot a y=e^x function Follow 1,073 views (last 30 days) Monica DelaCruz on 24 Feb 18 Vote 0 ⋮ Vote 0 Edited Stephen Cobeldick on 24 Feb 18 I have the task to plot a graph using the function y=e^x but I am having trouble with the constant e Do I have to define e first?
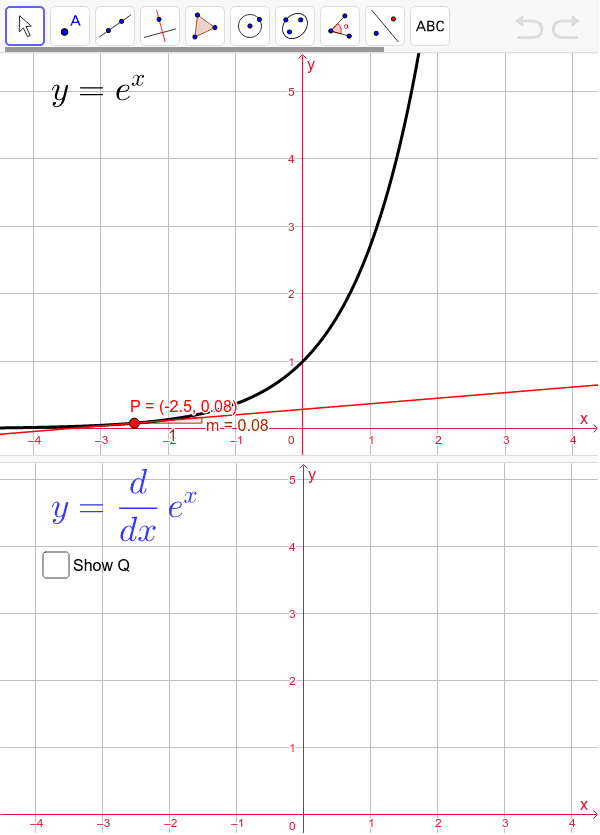



Derivative Of E X Geogebra
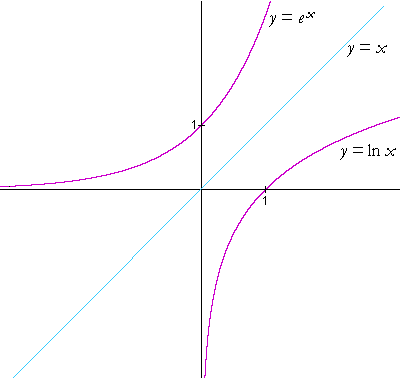



Logarithmic And Exponential Functions Topics In Precalculus
(sqroot)y=x is what that would be rearanged in terms of x so now y=e^x you can rearange that to lny=x Source(s) 2 years of IB HL maths 0 2 Anonymous 1 decade ago the inverse function of e^x is defined as ln(x), or log to the base e of x, or just natural logarithm the inverse function of n^x is ln(x)/ln(n) 0 2Free Maclaurin Series calculator Find the Maclaurin series representation of functions stepbystepFree logarithmic equation calculator solve logarithmic equations stepbystep




Mathematics Ii Tranquileducation




Find An Equation Of The Tangent To The Curve Y E X That Is Parallel To X 4y 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
Y = e^x, y = 0, x = 0, x = 1;2x2y=4 Geometric figure Straight Line Slope = 1 xintercept = 2/1 = 0000 yintercept = 2/1 = 0000 Rearrange Rearrange the equation by subtracting what is to the right of theExperiment with the scales to find the crossover point The function ln x increases more slowly at infinity than any positive (fractional) power Plot y = ln x and y = x 1/5 on the same axes Make the x scale bigger until you find the crossover point




Lesson 52 Derivatives Of Exponential Functions




Pdf Conditional Probability Panezai Khan Academia Edu
It is also the unique positive number a such that the graph of the function y = a x has a slope of 1 at x = 0 The (natural) exponential function f(x) = e x is the unique function which is equal to its own derivative, with the initial value f(0) = 1 (and hence one may define e as f(1))The natural logarithm, or logarithm to base e, is the inverse function to the natural exponential functionAsk Question Asked 5 years, 11 months ago Active 5 years, 11 months ago Viewed 35k times 3 2 $\begingroup$ I am studying probability and trying to follow an example in my textbook discussing expectation of the sum of random variables But I'm having trouble following itHow to understand the proof of EXY = EX EY?




E X 1 Ed E X 1




Chislo E Funkciya U E X Eyo Svojstva Grafik Differencirovanie Urok Algebra 11 Klass
Experiment with the scales to find the crossover point The function ln x increases more slowly at infinity than any positive (fractional) power Plot y = ln x and y = x 1/5 on the same axes Make the x scale bigger until you find the crossover pointGet the answer to Range of y=e^x with the Cymath math problem solver a free math equation solver and math solving app for calculus and algebraOpen up a spreadsheet in Excel Put the numbers 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3 into column A starting in cell A1 In cell B1 type




Solution Locate The Points Of Inflection Of The Curve Y F X X 2



Logarithmic Functions Their Graphs
LECTURE 12 Conditional expectations • Readings Section 43;Question Solve The Initial Value Problem Xy' Y = E^x, Y(l) = 2,t >0 This problem has been solved!Exponential functions are a special category of functions that involve exponents that are variables or functions Using some of the basic rules of calculus, you can begin by finding the derivative of a basic functions like a x {\displaystyle a^{x}} This then provides a form that you can use for any




Mse And Bias Variance Decomposition By Maksym Zavershynskyi Towards Data Science



Emat6680 Gif Exponential Functions By Hee Jung Kim Let S Start With A Number E Mathematician Euler Used The Letter E For The First Time So It Is Sometimes Called Euler S Number The Number E Is Defined By The Following Equation For Any Positive Integer N If
Calculus Integral with adjustable bounds example Calculus Fundamental Theorem of CalculusEY = E (X EX)2 = var(X) We have then P(jX EXj ) = P((X EX)2 2) = P(Y 2) EY 2 = var(X) 2 (1) Independence and sum of random variables Two random variables are independent independent if the knowledge of Y does not in uence the results of Xand vice versa This 3Var(XjY =y)=E(X2jY =y)¡E(XjY =y)2 Remark We always suppose that åx jg(x)jfXjY(xjy)•¥ Definition Denote j(y) = E(XjY = y) Then E(XjY) def= j(Y) In words, E(XjY) is a random variable which is a function of Y taking value E(XjY =y) when Y =y The E(g(X)jY) is defined similarly In particular E(X2jY) is obtained when g(X)=X2 and Var




The Curve Of Exponential Function Y A X A X E X If A E And X 0 Download Scientific Diagram



Area Of A Surface Of Revolution
This might feel a bit more difficult to graph, because just about all of my yvalues will be decimal approximationsBut if I round off to a reasonable number of decimal places (one or two is generally fine for the purposes of graphing), then this graph will be fairly easy



Logarithms



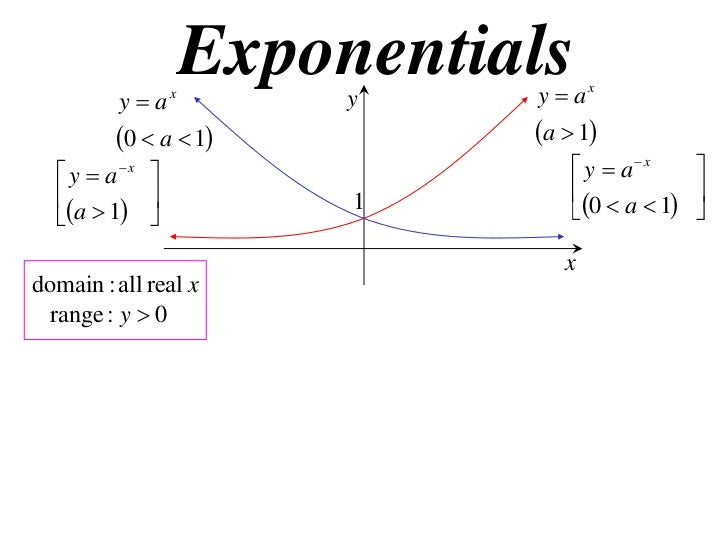
Exponential Functions Definition Formula Properties Rules




Xy 1 X Y E X Sin 2x 1st Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Youtube




E Xy E X E Y And Pull Out Property Of Conditional Expectation Without Standard Machine Mathematics Stack Exchange



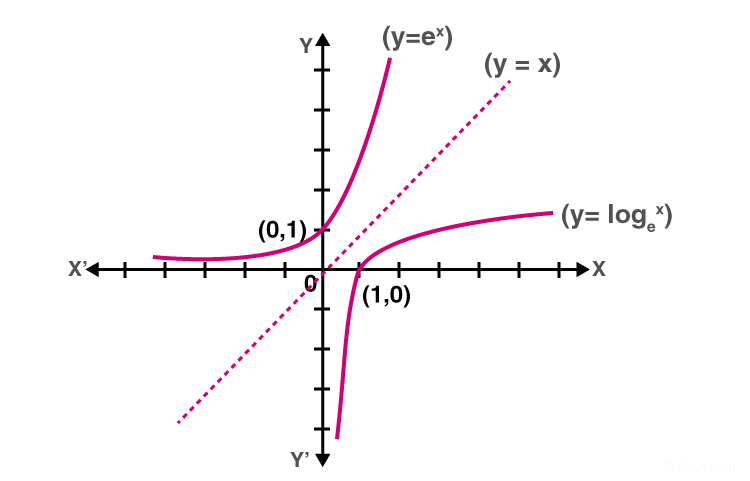
Fungsi Eksponen Dan Logaritma
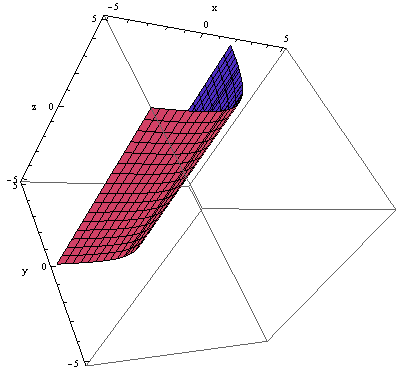



Sketch The Graph Of Y E X As A Surface In R 3 Homework Help And Answers Slader



Gaussian Integral Wikipedia




đạo Ham Của E Mũ X Va E Mũ X La Gi
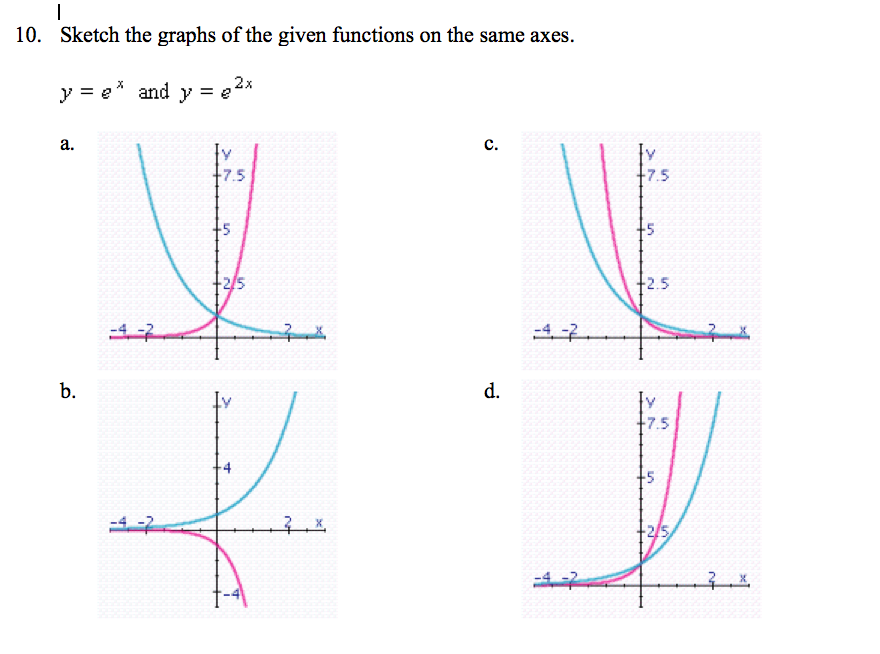



Solved Sketch The Graphs Of The Given Functions On The Sa Chegg Com




Find F X That Minimizes E Y F X 2 X Mathematics Stack Exchange



Content Graphing Logarithmic Functions



Graphically Determine The Derivative Of Y E Ax Geogebra



12x1 T02 01 Differentiating Exponentials
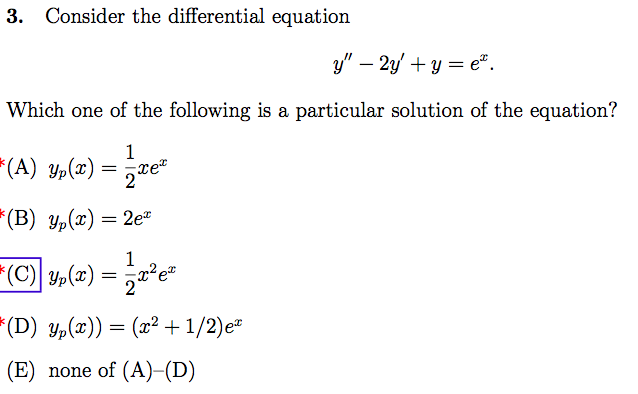



Solved Consider The Differential Equation Y 2y Y Chegg Com



Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra



What Is The Domain And Range Of Y E X Socratic



Plot A Function Y F X In Python W Matplotlib



Arc Length




How To Show That E E X Mid Y Mid Y E X Mid Y Mathematics Stack Exchange




指数関数 対数関数




Resuelva Por Coeficientes Indeterminados Y Variacion De Parametros By Gerson Villa Gonzalez Issuu




E X 0




Y E X图像 第1页 一起扣扣网



Solution Y E X How Do I Graph This Please Help




Find The Angle Between The Curve 2y E X 2 And Y Axis Brainly In



How To Sketch The Graph F X E X 1 Socratic
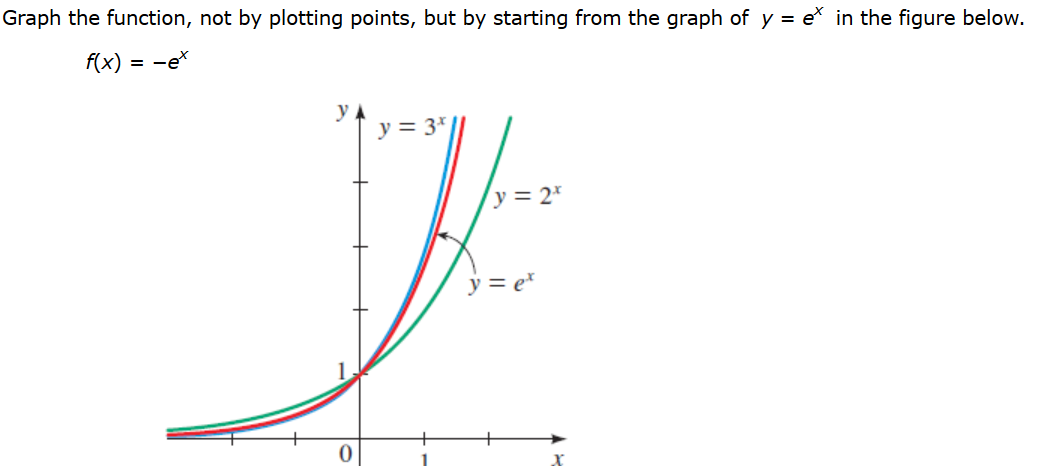



Solved Graph The Function Not By Plotting Points But By Chegg Com




Introduction We Are Going To Look At Exponential Functions We Will Learn About A New Special Number In Mathematics We Will See How This Number Can Be Ppt Download




A Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Curve In R2 B Sketch The Graph Of Y Ex As A Surface In R3 C Describe And Sketch The Surface Z Ey Study Com



How To Find X And Y Intercepts Of Graphs




Solved Solve The Differential Equations Y Y E X C Chegg Com



Ilectureonline



Find The Exact Coordinates Of The Centroid Where Y E X Y 0 X 0 X 3 Mathskey Com




The Logarithm And Exponential Functions
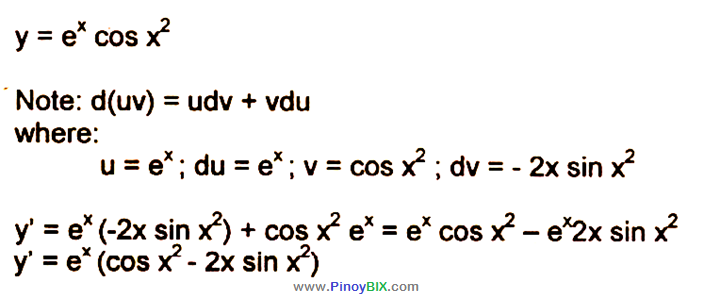



Solution Differentiate Y E X Cos X 2




Sketch The Region Enclosed By The Curves And Find Its Area Y E X Y E 4 X X 0 X Ln 2 Enter The Exact Answer As An Improper




If Y Ex Cosx Prove That Dy Dx 2 1 2 Ex Cos X Pi 4 Math Meritnation Com
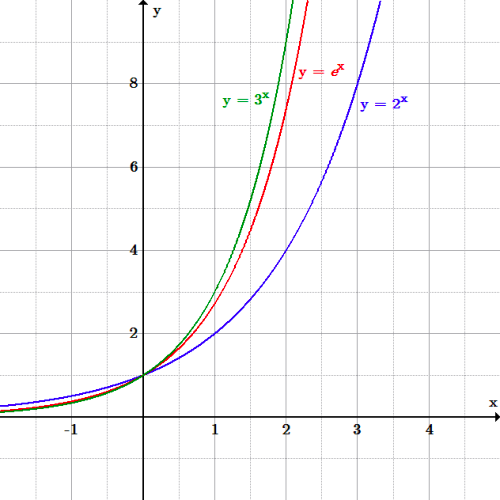



The Real Number E Boundless Algebra



What Is The Graph Of E X Quora



7 1 The Natural Exponential Function



How Do You Find The Equation Of The Tangent Line To The Curve Y E X Sin X At Point 0 0 Socratic



Solution Use The Graph Of Y E X To Evaluate E 1 6 To Four Decimal Places




15 6 Calculating Centers Of Mass And Moments Of Inertia Mathematics Libretexts



Use Of Log Log Plane And Semi Log Plane



Function And Relation Library




Dy Dx 2y E 2x Sinx Given That Y 0 When X 0
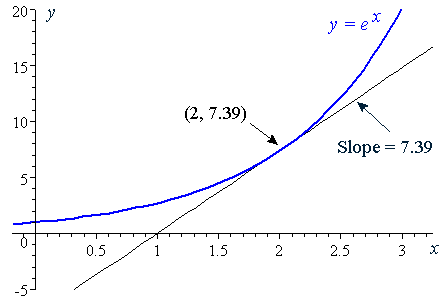



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function
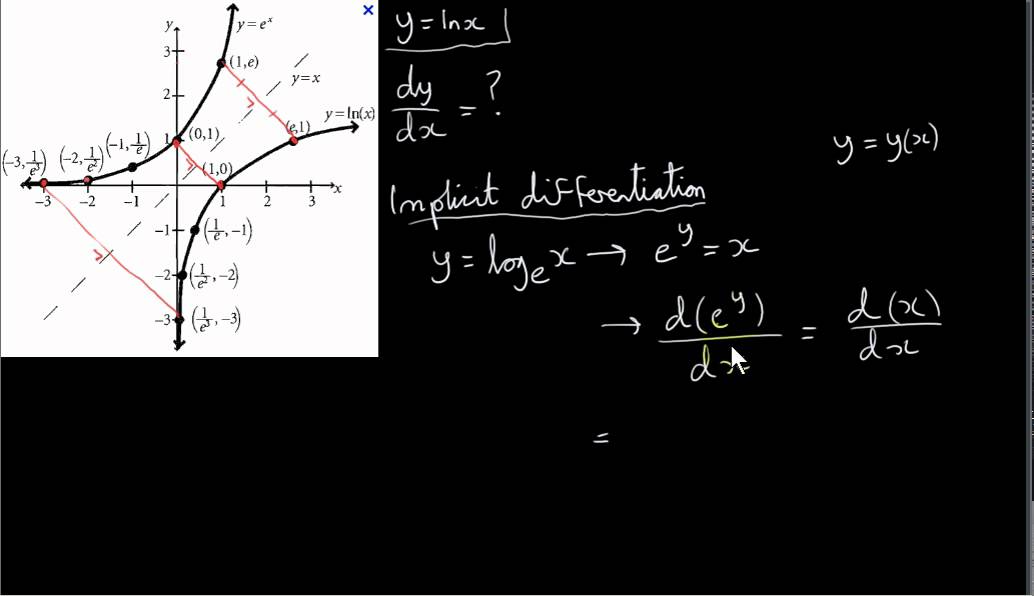



The Functions Y E X And Y Ln X Youtube
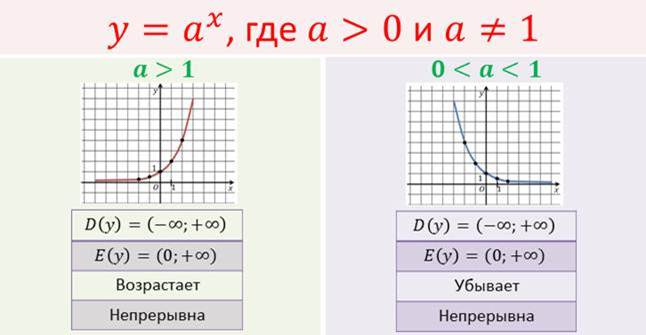



Chislo E Funkciya Y E X Ee Svojstva Grafik Diff




If Y Ex Sin X Prove That D2y Dx2 2 Dy Dx 2y 0 Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 5p09j033




Ppt X Y 2 X 2 Y 2 2 Xy E X Y 2 E X 2 E Y 2 2 E Xy Powerpoint Presentation Id



If X Y E X Y Show That Dy Dx Logx Log Xe 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




File Graph Y E To 0 5x Lin Lin Png Wikimedia Commons




How To Celebrate E Day Feb 7 18 With The Mathematical Constant




Transforation Of Exponential Graphs Y Ex Matching Cards With Answers Teaching Resources



Experiment 2 Working With Logarithmic Scales




Exponential Functions Ck 12 Foundation




Proof The Derivative Of 𝑒ˣ Is 𝑒ˣ Video Khan Academy




If X Y E X Y Then Dy Dx Is




The Graph Of Y E X Is Transformed As Shown In The Graph Below Which Equation Represents The Brainly Com




Find The Radius Of Curvature Of The Curve Y E X At The Point Where It Crosses The Y Axis Math Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com



Experiment 2 Working With Logarithmic Scales
コメント
コメントを投稿